|
|
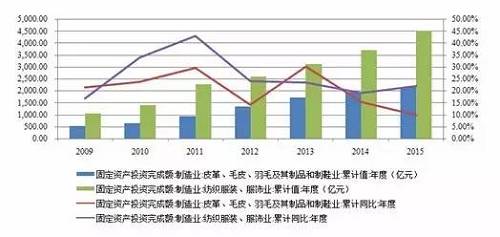
2016 Research Report on Credit Risk in the Clothing and Home Textile Industry1、 Industry definition Clothing and home textiles refer to the production and sales of clothing and home textile products. Pengyuan Credit Rating Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Pengyuan" or "we") shall identify a clothing and home textile enterprise based on the following criteria: When the proportion of operating revenue from the company's clothing and home textile products is greater than or equal to 50%, it shall be classified into the clothing and home textile industry; When the proportion of operating revenue from the company's clothing and home textile products is less than 50%, but their revenue and profit both account for a proportion * in the business structure, and both account for 30% or more of the company's operating revenue and profit, they are also classified as the clothing and home textile industry. 2、 Industry Analysis The clothing and home textile industry has continuously expanded in scale, playing an important role in solving employment, export earnings, and other aspects, and is an important component of the national economy China is a clothing consumer and producer in the world. After experiencing high growth in 2010 and 2011, the growth rate of fixed assets investment in the clothing and home textile industry has dropped since 2012, but still maintained a rapid growth. In the past three years, the growth rate of fixed assets investment in the textile and clothing industry was 23.57%, 19.20% and 22.00%, respectively The growth rate of completed fixed assets investment in feather and its products and footwear industry was 30.31%, 15.60% and 10.00% respectively. Compared to other industries, the clothing and home textile industry is characterized by relatively small investment, relatively low technological content, and relatively fast investment returns. Therefore, the clothing and home textile industry is still actively encouraged to invest in some places, especially in the central and western regions. Figure 1 China's textile and clothing industry and fixed assets investment
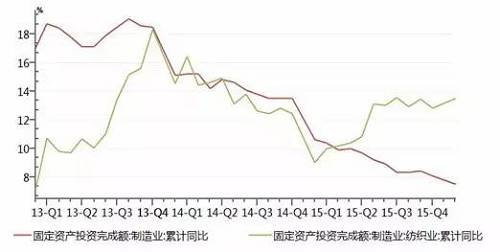
Source: Wind, compiled by Pengyuan Driven by the rapid growth of the clothing and home textile industry, China's textile industry investment continues to grow, and the industry scale is still expanding. According to the data of the National Bureau of Statistics, in 2015, China's textile industry completed 1191.3 billion yuan of fixed assets investment in projects with more than 5 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 15.0%, * 6.9 percentage points higher than the national manufacturing industry's 8.10% growth level in the same period. The expansion of clothing, home textile and textile manufacturing industry has provided a large number of jobs. According to statistics, for every billion yuan of fixed assets investment, 932 people can be employed on average, while 1876 people and 4464 people can be employed on textiles and clothing respectively. By the end of 2015, there were 20500 textile enterprises and 4.487 million textile industry employees nationwide, which played a significant role in solving the employment problem of residents. Figure 2 Growth rate of fixed assets investment in textile industry from 2013 to 2015 (unit:%)
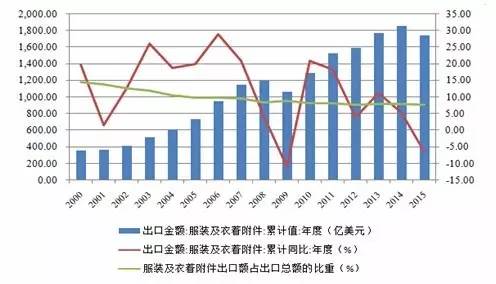
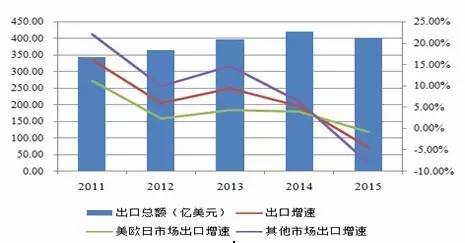
Source: Wind, compiled by Pengyuan As a major exporter of clothing in the world, China occupies an important position in international clothing trade, and the clothing industry has been a major exporter of foreign exchange for many years. In 2000, China's clothing and clothing accessories exports amounted to US $36.20 billion, and in 2015, they reached US $174.28 billion. During the past 15 years, China's exports increased by 4.84 times, becoming a major producer and exporter of global textiles and clothing products. Figure 3 Export of China's clothing and clothing accessories from 2000 to 2015
Source: Wind, compiled by Pengyuan
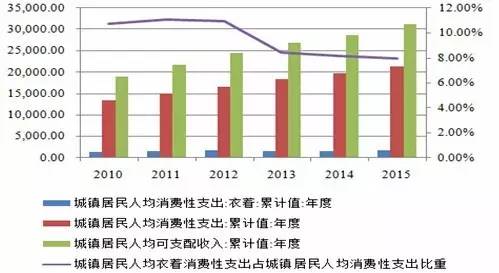
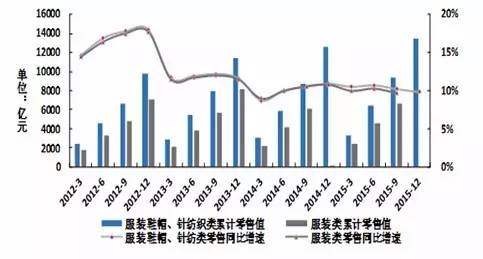
In the future, China's overall economic environment will not change significantly in the short to medium term, and the clothing and home textile industry may maintain a certain growth rate. The clothing and home textile industry will still occupy a relatively important position in the national economy. Affected by factors such as slowing economic growth in domestic and foreign markets, adjustment of domestic residents' consumption structure, and exchange rate fluctuations, the market demand for clothing and home textile industry has weakened (1) Domestic market In recent years, China has continuously promoted the process of urbanization. By the end of 2015, the urban population in China had reached 771 million, and the urbanization rate reached 56.10%, with a year-on-year increase of 1.33 percentage points; The per capita disposable income and consumption expenditure of urban residents have steadily increased. In 2015, the per capita disposable income of urban residents in China was 31195 yuan, an increase of 8.15% compared to the same period last year. In 2015, the per capita consumption expenditure of urban residents in China was 21392 yuan, an increase of 7.13% compared to the same period last year. The improvement of residents' income level has created certain favorable conditions for increasing the demand for clothing consumption. However, due to the increasing proportion of residential and medical expenses in the residents' consumption structure, the proportion of per capita clothing consumption expenditure of urban residents in China has continued to decline since 2012, and in 2015, the proportion decreased to 7.95%. With the development of urbanization and the improvement of per capita disposable income, the sales value of China's clothing industry continues to grow. However, in terms of growth rate, due to factors such as macroeconomic downturn, consumption structure adjustment, and slowing domestic demand growth, the growth rate of clothing retail sales has shown a downward trend since 2014. Figure 4 Proportion of per capita disposable income, expenditure, and clothing consumption of urban households in China (unit: yuan)
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan Figure 5 Domestic textile and clothing retail sales from 2012 to 2015
Source: Official website of the National Bureau of Statistics, compiled by Peng Yuan (2)Foreign market Since 2014, the exchange rate of the RMB has continued to depreciate. As of October 12, 2016, the exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar was 6.73, a new low in six years. In theory, the continuous depreciation of the RMB has provided certain good external conditions for China's clothing export enterprises. However, compared to the RMB, Southeast Asian countries have a stronger devaluation of their currencies, coupled with cheaper labor and other costs. When relevant enterprises sign export orders, the International Chamber of Commerce takes into account the depreciation of the RMB to lower prices. Therefore, the decline in the exchange rate has a very limited effect on stimulating the growth of China's textile and clothing exports. Since March 2015, China's clothing export situation has not been very optimistic. As can be seen from the figure below, the export amount of clothing and clothing accessories has been in a negative growth state. The growth rate of domestic textile product exports has slowed down year by year since 2013 and has shown a negative growth. According to statistics from China Customs, China's domestic textile product exports totaled $40.23 billion in 2015, a year-on-year decrease of 4.4%. Figure 6 The growth rate of China's RMB exchange rate and clothing exports in recent years
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan Figure 7 Export situation of domestic textile products in China
Source: Official website of China Home Textile Association, compiled by Peng Yuan
Affected by the implementation of the "the Belt and Road" strategy and the deepening of China Africa cooperation, China's exports to some emerging markets have achieved rapid growth, and new export markets are being explored and cultivated. According to customs statistics, from January to November 2015, China's clothing exports to Africa increased by 10.84% year-on-year, accounting for 5.78% of the total export value, an increase of 0.96 percentage points compared to the same period in 2014; Among the countries along the "the Belt and Road", China's clothing exports to South Korea, the United Arab Emirates, the Philippines, Israel, Jordan and Iran increased by 17.05%, 14.92%, 45.69%, 20.31%, 66.69% and 32.75% respectively. However, the total export value of the five countries is 15.034 billion US dollars, accounting for only 9.48% of China's total export value, with little impact on the overall export situation. Figure 8 China's exports to some emerging markets from January to November 2015
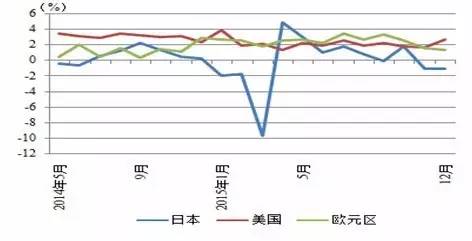
Data source: China Customs The weakening of the RMB exchange rate and the rapid growth of exports from some emerging markets have limited short-term impact on China's textile exports, and the consumption capacity of the international market is the key. The traditional export destinations of China's clothing and home textiles are mainly concentrated in the United States, Europe, and Japan. The economic conditions of the United States, Europe, and Japan directly affect China's clothing and home textile exports. Since the financial crisis, the economies of the United States, Europe, and Japan have been severely affected. Although they have gradually recovered in recent years, they have only moved forward slowly. In terms of consumption, in 2015, the retail sales in the United States increased by 2.6% year-on-year, 1.2 percentage points higher than the same period in 2014; Japan's retail sales fell 1.1% year-on-year; Retail sales in the euro area increased by 1.4% year-on-year, down 1.5% from the same period last year. Figure 9 Year-on-year growth rate of retail sales in the three major economies from May 2014 to December 2015
Source: National Bureau of Statistics, compiled by Peng Yuan
The rebound in GDP growth and consumption growth in the United States have created a good external environment for China's clothing and home textile exports, but the markets in Europe and Japan are still sluggish, affecting the overall growth of China's clothing exports. According to national customs data, China's textile, clothing, and clothing accessories exports in 2015 amounted to $174.28 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 6.4%. Among them, exports to the United States increased by 6.7% year-on-year, exports to the European Union decreased by 9.3% year-on-year, and exports to Japan decreased by 11.6% year-on-year. At the same time, in recent years, there have been continuous trade frictions between China and the United States, with trade imbalances, textile special protection, and anti-dumping against China constituting the main content of trade frictions between China and the United States, which will continue to have a negative impact on China's foreign trade. The continuous decline in the growth rate of clothing exports is related to factors such as insufficient demand in the international market, the sharp depreciation of the euro and the yen, and the outward transfer of domestic production capacity leading to trade transfer. In addition to the above factors, clothing exports in the future will also be affected by the liberalization of global regional trade. China's clothing exports may become a new normal with slight or zero growth or even negative growth. The market entry threshold for the clothing and home textile industry is low, there are many enterprises in the industry, and the competitive pressure is increasing The clothing and home textile industry is a labor intensive industry with low market entry barriers and a large number of enterprises in the industry. As of the end of 2015, there were 15585 domestic textile and clothing enterprises, with a compound growth rate of 8.69% from 2011 to 2015. Men's wear is an important component of the clothing market. China's men's wear industry has formed a "Zhejiang style" men's wear industrial cluster represented by Shanghai, Ningbo, and Wenzhou in the Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai regions, a "Fujian style" men's wear industrial cluster represented by Jinjiang and Shishi in southeast Fujian, and a men's wear industrial cluster in the Pearl River Delta in southern Guangdong that has grown independently with overseas advantages such as Hong Kong and Macao. After more than 30 years of development, China's men's clothing industry as a whole is in a state of complete competition, with a wide range of brands on the market. Domestic men's clothing brands include Sevenwolves (002029, stock bar), Baoxiniao (002154, stock bar), Hinur (002485, stock bar), Youngor (600177, stock bar), Red Bean (600400, stock bar), Jiumu * (601566, stock bar), and Shanshan. Currently, international brands are mainly concentrated in the high-end market in first and second tier cities, while domestic men's wear brands are mainly in second and third tier cities. Driven by the rapid expansion of the consumer market, the domestic men's wear market has grown rapidly. However, due to low barriers to entry, numerous domestic men's wear manufacturers, and the impact of the financial crisis leading to sluggish demand and the entry of a large number of international brands into the domestic market, the competition in the men's wear market in China has intensified. According to data from China National Business Information, in 2014, the sales of men's clothing products of 100 large retail enterprises nationwide decreased by 3.10% year-on-year. In 2015, the sales of men's clothing products by large retail enterprises nationwide decreased by 1.2% year-on-year, while the retail sales of clothing products decreased by 0.3% year-on-year. According to the "2015 China Garment Industry Consumption Trend Research Report" released by Taobao, in terms of consumers, the overall gender ratio in the clothing industry is about one to three, with women as the consumer group. The women's clothing market has a high degree of segmentation and low market concentration. According to Euromonitor statistics, the retail sales of women's clothing in China in 2014 were approximately 85 billion yuan, while the total market share of the top ten high-end women's clothing brands was only 25.2%, resulting in significant market competition pressure. In the women's clothing value chain, design accounts for about 40%, marketing channels account for about 50%, and production accounts for about 10%. That is, design and marketing are at the top of the clothing value chain, and production and processing are at the bottom of the value chain. Although China's women's clothing has cost advantages in the production and processing field, there is still a significant gap between China and the international advanced level in terms of research and development design, sales channels, and brand operation. Despite this, a small number of local brands have also initially formed in the domestic women's clothing industry, such as Masefield, Langzi, Vignes (603518, stock bar), Gliese (603808, stock bar), and Kletier (Hong Kong). This type of enterprise mainly engages in independent brand women's clothing, with strong R&D and design capabilities. After years of development and accumulation, it has established a relatively complete marketing network, has a certain popularity and relatively stable consumer group, and gradually established a competitive advantage. According to the "Domestic Youth Leisure Wear Industry and Market Analysis Report" released by the China Textile Planning and Research Association, the youth leisure wear industry can be divided into two categories: one, two, and three, four. From the perspective of market structure, international brands are basically concentrated in the first and second categories of markets, with their brands and prices positioned at the mid to high-end end, and have high requirements for store design. It is expected that international brands will not penetrate into the third and fourth categories of markets in the short term. Independent brands such as Meibang, Sema, and Yichun have developed in China for many years, and have established relatively complete marketing networks in the first and second class markets, becoming the leading force in the domestic first and second class markets. However, with the influx of more and more international leisure brands, as well as the gradual penetration of sports brands such as Adidas and Nike into leisure clothing, the degree of competition in the first and second categories of markets continues to intensify, and the profitability of independent brands in the first and second categories of markets gradually decreases. Therefore, some independent brands with brand advantages, financial strength, and cross regional business capabilities have begun to penetrate into the third and fourth categories of markets. Compared with sports and leisure apparel such as Adidas and Nike, fashion and leisure apparel such as Meibang and Sima have more brand advantages. In recent years, they have continuously developed low-cost products to seize the low-end market. The price advantage of independent brands in three or four categories of markets will decline, and the competitive pressure will continue to increase. In the face of fierce industry competition, the drawbacks of extensive development relying on traditional extension channels to expand into * have gradually emerged in China. Some clothing enterprises have experienced a decline in profits and a surge in inventory. Baozi, a brand that has been in the high-end women's clothing industry, was also acquired and delisted in 2015 due to poor management. Affected by intensified industry competition and rising costs in the clothing and home textile industry, the growth rate of profit level of clothing enterprises has slowed down, and the operating performance of major enterprises in the industry has differentiated Due to the increasing competition in the industry, some businesses have increased their discount efforts, and in recent years, the factory price index of clothing products has been continuously declining. From the perspective of cost, both raw materials, sales expenses, and labor costs have shown varying degrees of increase.
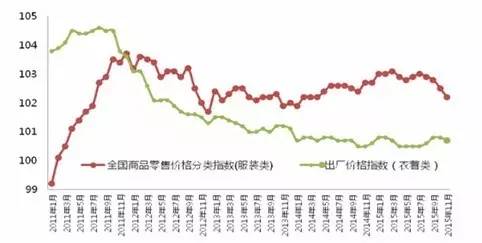
Figure 10 Changes in the consumer price index of clothing
Source: National Bureau of Statistics, compiled by Peng Yuan
In terms of raw materials, the overall price of clothing fabrics and clothing accessories in China has shown an upward trend in recent years. Taking the Keqiao Textile Price Index as an example, the price indexes of Keqiao textile clothing fabrics and clothing accessories have increased from 98.97 and 93.23 at the beginning of 2010 to 116.91 and 125.89 at the end of 2015, with a compound growth rate of 3.39% and 6.19% in 2010-2015, respectively. The rise in the prices of raw materials such as fabrics has increased the operational pressure on the clothing industry. At the same time, in recent years, the increasing rent, channel costs, and labor costs have also squeezed the profits of the clothing industry. According to the results of a special survey conducted by the China Garment Association on the operating costs of clothing enterprises, the operating costs of clothing enterprises have gradually increased, with labor costs rising the fastest, especially the labor costs of sewing workers. In the past decade, the amount of social security has increased rapidly. Despite the current oversupply of labor in China, due to the large proportion of migrant workers in various textile enterprises, "difficult recruitment" is still a major problem that the textile industry faces every year. For example, among the more than 4000 textile shoes and hats enterprises in Changzhou, Jiangsu Province, the number of migrant workers exceeds 500000, accounting for nearly one-third of the 1.6 million migrant workers in the entire region. In recent years, the gap of migrant workers in the Pearl River Delta region has significantly increased, while the number of migrant workers in cities in the Yangtze River Delta region such as Shanghai and Hangzhou is gradually increasing. In addition, over the years, various regions have continuously raised wage standards, raising labor costs in the textile industry.
Figure 12 Monthly * wage standards in major regions of China (yuan/month)
Source: Wind, compiled by Pengyuan
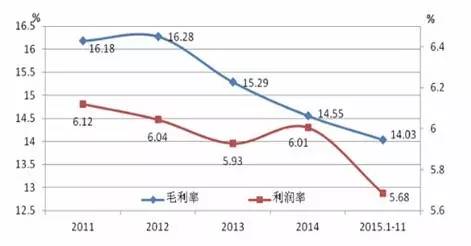
Affected by the continuous decline in product prices and rising costs, the overall profitability of the clothing industry has continued to decline. The industry's gross profit margin has continued to decline from 16.28% in 2012 to 14.03%, and the profit margin has decreased from 6.04% to 5.68%.
Figure 13 Changes in profit margins in the clothing industry
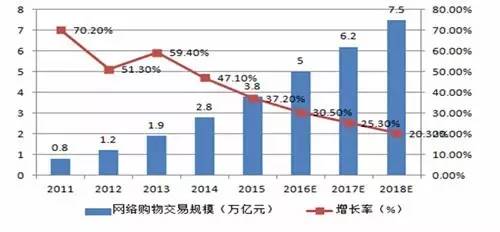
Source: National Bureau of Statistics, compiled by Peng Yuan Against the backdrop of a decline in overall profitability, the performance of large clothing enterprises is relatively stable, while the performance of small enterprises fluctuates significantly, with a more pronounced polarization in profitability. For example, in the men's wear industry, two companies, Hailan Home and Youngor, achieved a total operating income and net profit of 17.229 billion yuan and 4.843 billion yuan, respectively accounting for 73.38% and 86.18% of the men's wear operating income and net profit, with an average net profit margin of 28.10%. Among the other nine companies, 8 had a decrease in net profit, while 3 had losses. Among the profitable companies, the net profit * was 27 million yuan, * was 266 million yuan. Companies such as "La Chapelle" in women's wear, "Sima Clothing" in casual wear, and "Anta" in sportswear are all in a * position in their respective fields of profitability, with a relatively high market share. The development of e-commerce and the liberalization of relevant policies have brought new challenges and opportunities In recent years, China's e-commerce has developed rapidly, with the gradual rise of online shopping and the rapid growth of total online consumption. From 2014 to 2015, the total online retail sales nationwide were 2789.8 billion yuan and 3877.3 billion yuan, with year-on-year growth of 49.70% and 33.30%, respectively. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, online retail sales of clothing goods increased by 21.4% year-on-year. Representative domestic merchants include Taobao, Tmall, JD.com, etc. According to Alibaba's financial report, as of June 30, 2015, the annual active buyers on China's retail commerce platform reached 367 million, a year-on-year increase of 32%, with an average of over 50 orders placed by active users per year. As of March 31, 2016, the annual active buyers of Chinese retail platforms had increased to 434 million, and the total global transaction volume of Tmall * in 2016 exceeded 120.7 billion yuan. In the next few years, there is still great room for growth in China's online retail market. According to research data from iResearch Consulting, online retail currently accounts for only 7.9% of the total retail market in China; By 2016, the penetration rate of China's online retail market is expected to reach 11.5%, with a scale of 3.79 trillion yuan. In addition, with the construction of a nationwide logistics system and the upgrading of broadband networks in urban and rural areas, the use of smartphones and portable tablets has become increasingly common, and various types of online shopping APP applications have also become increasingly perfect. In this context, the consumption habits of domestic consumers are gradually changing, and the willingness to purchase goods through the Internet will be further enhanced. Figure 14 Transaction Scale of China's Online Shopping Market from 2011 to 2018
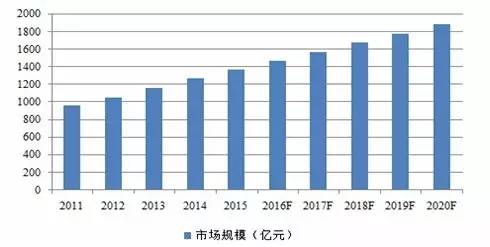
Source: China Industry Information Network, compiled by Peng Yuan The baby boom is approaching and the full liberalization of the second child policy will unleash the market potential of children's clothing. From the perspective of the industrial life cycle, China's children's clothing industry is still in the growth stage, with rapid market demand growth and increased growth space. According to the data of the sixth national population census, the population aged 0-14 years in China is 222 million, accounting for 16.6% of the total population, including about 100 million urban children, which are the main groups of children's clothing consumption at present; At the same time, the 1980s was the third peak period of birth in China, with a total population of 220 million. This was the third baby boom in China. The average marriage ages of Chinese men and women are 25.5 and 23.5 years, respectively. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, China's fertility peak is between 20-34 years old, with 25-29 years old. The baby boom of 1985-1995 will enter the stage of marriage and childbirth, with approximately 11 million couples registered annually. China will usher in a fourth baby boom. The number of children determines the consumption capacity of the children's wear market. In recent years, the consumption scale of children's wear in China has continuously expanded and maintained a high growth rate. According to the "2016-2021 China High End Children's Wear Industry Research and Investment Prospect Prediction Report" released by the China Commercial Industry Research Institute, with the opening up of second birth and consumption upgrading, the size of China's children's wear market is expected to exceed 180 billion yuan by 2020. Affected by the rapid growth of demand, the price of children's clothing has shown a continuous upward trend. According to the statistics of China National Business Information *, the unit price of children's clothing in large retail enterprises nationwide has increased by 19.4% from 2011 to 2015, with an average annual growth of 4.5%. Figure 15 Market Size of Children's Wear
Data source: China Commercial Industry Research Institute, compiled by Peng Yuan
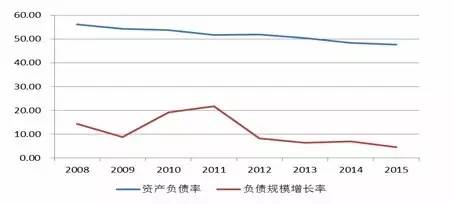
3、 Analysis of changes in financial risks of enterprises in the industry (1) Data selection We have selected a total of 15 enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry that have issued bonds as of September 30, 2016 as our analysis samples (hereinafter referred to as "sample enterprises", see the appendix for details). (2) Analysis of changes in corporate financial risks The growth rate of the overall debt scale of the clothing and home textile industry has continued to decline, and the degree of debt operation has also shown a downward trend. However, the degree of debt operation of enterprises with strong financing capacity in the industry has increased, and the pressure on debt repayment has increased Since 2008, the debt financing scale of the textile and clothing industry has continued to expand, and the growth rate of debt scale has been positive. As of the end of June 2016, the average debt scale of the entire industry was 37943300 yuan. From the perspective of the growth rate of debt scale, from 2009 to 2011, the growth rate of debt scale increased year by year, while after 2012, the growth rate of debt scale decreased year by year. From the perspective of asset liability ratio, since 2008, the asset liability ratio of the textile and clothing industry has continued to decline, and the degree of debt operation of the entire industry has shown a downward trend. Figure 16 Liabilities of China's textile and clothing industry in recent years (Unit:%)
Source: Wind Information, China Industry Information Network, compiled by Pengyuan As for the sample enterprises, from the perspective of debt scale, the average debt scale of the selected 15 sample enterprises is relatively large, and the growth rate of debt scale has increased year by year since 2012. At the end of 2015, the average debt scale reached 5.938 billion yuan, an increase of 29.22% compared to the previous year. From the perspective of asset liability ratio, in recent years, the average asset liability ratio of sample enterprises has also shown a rising trend year by year. As of the end of 2015, the average asset liability ratio was 47.14%, an increase of 4.09 percentage points compared to the previous year, and the degree of liability management has increased. Whether viewed from the growth rate of debt scale or asset-liability ratio, the performance of the sample enterprises is contrary to the overall trend of enterprises in the entire industry. We believe that the main reason is that the majority of the sample enterprises are high-quality enterprises in the industry, with strong comprehensive competitive strength, strong demand for business expansion, and their strong ability to conduct debt financing through banks or capital markets, as well as lower financing costs, which also promote enterprises to have more motivation to conduct debt operations. Figure 17 Liabilities and asset-liability ratio of sample enterprises in recent years
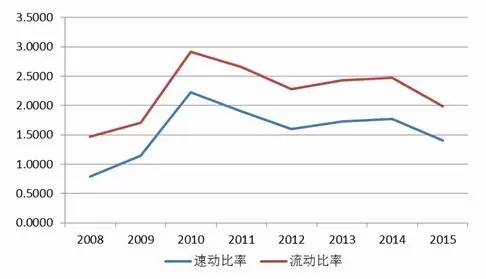
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan The sample enterprise is a relatively high-quality enterprise in the industry, with strong debt financing capacity. The expansion of debt financing scale has led to an increase in the degree of debt operation, resulting in a decrease in the enterprise's debt repayment ability indicators, and an increase in debt repayment pressure. Figure 18 Current ratio and quick ratio of sample companies in recent years
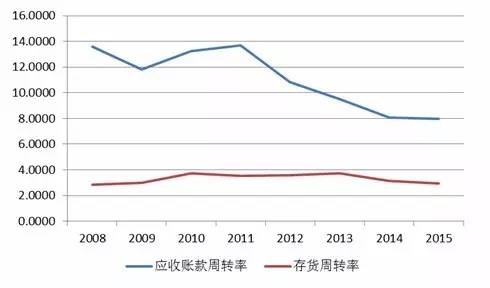
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan The inventory turnover rate and accounts receivable turnover rate of the clothing and home textile industry have decreased, and the efficiency of asset operation has decreased Affected by factors such as slowing economic growth in domestic and foreign markets, exchange rate fluctuations, and trade friction, the market demand in the textile and clothing industry has weakened. Affected by this, the inventory size of enterprises in the textile and clothing industry has increased in recent years, and the inventory turnover rate has decreased; From the perspective of the turnover rate of accounts receivable, the turnover rate of textile and clothing accounts receivable has decreased slightly in recent years, and downstream customers have formed a certain occupation of the accounts of the industry. Figure 19 The turnover rate of accounts receivable and inventory in the textile and clothing industry in recent years
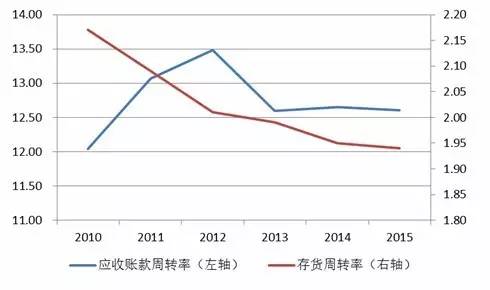
Source: Wind Information, Pengyuan Collation From the perspective of the accounts receivable turnover rate and inventory turnover rate of the sample enterprises in recent years, after 2010, the accounts receivable turnover rate of the sample enterprises showed a downward trend, and the inventory turnover rate also decreased. In recent years, sample enterprises have still actively expanded the market, resulting in a significant increase in inventory size and accounts receivable. However, due to the weakening market demand in the domestic and foreign clothing and home textile industries, the inventory turnover rate of sample enterprises has decreased, and the recovery cycle of accounts receivable has extended, increasing the pressure on enterprise capital turnover. Figure 20 Receivable turnover rate and inventory turnover rate of sample enterprises in recent years
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan
The fierce competition in the industry has led to the elimination of loss-making enterprises and the development of high-quality enterprises. However, rising costs and weakening demand have reduced the gross profit margin and profitability of the clothing and home textile industry The concentration of enterprises in the textile and clothing industry is relatively low. In 2008-2010, due to the impact of the market environment, some loss-making enterprises were gradually eliminated, resulting in a decrease in the proportion of loss-making enterprises in the textile and clothing industry to the total number of enterprises, from 22.77% in 2008 to 9.67% in 2011. After 2011, the proportion of loss-making enterprises in the textile and clothing industry to the total number of enterprises in the industry was relatively stable, maintaining around 11%. Figure 21 Proportion of loss-making enterprises in the textile and clothing industry in recent years
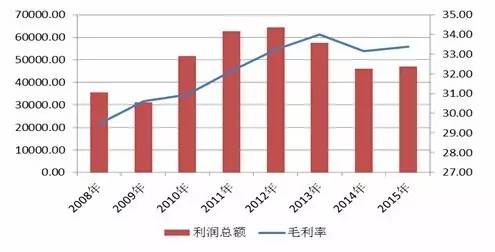
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan In recent years, the rising prices of raw materials in the upstream of the textile and clothing industry and the increase in labor costs have compressed the industry's profit margin. After 2012, the gross profit margin level of the textile and clothing industry has decreased year by year, and the profitability level of enterprises in the industry has decreased year by year. In 2015, the gross profit margin of the textile and clothing industry was 14.38%, down 0.4 percentage points year-on-year. From the perspective of the average total profit of enterprises in the industry, in recent years, the total profit of the industry has increased, especially after the elimination of some loss-making enterprises in 2010, the total profit has increased significantly. However, from the perspective of the growth rate of the total profit, affected by the macroeconomic slowdown, consumption growth slowdown, and intensified industry competition, the growth rate of the total profit has decreased year by year, and in 2015, the growth rate of the total profit has even dropped to a historical * level, only 4.00%, A year-on-year decrease of 6.55 percentage points. Figure 22 Gross profit margin level of textile and clothing owners' business in recent years
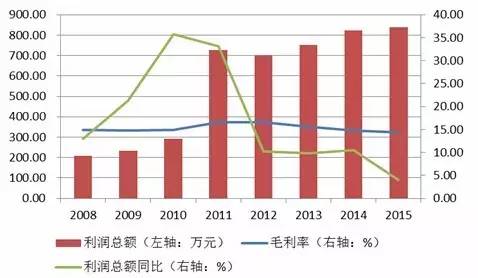
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan From the perspective of selected sample enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry, in 2009-2012, against the background of eliminating loss-making and backward enterprises in the industry, the total profit and gross profit margin levels of the sample enterprises increased year by year due to their strong strength. After 2012, affected by factors such as slowing economic growth in domestic and foreign markets, intensified competition, exchange rate fluctuations, trade friction, rising raw material prices, and increased labor costs, The average total profit and gross profit margin of the sample enterprises have decreased, but the overall gross profit margin is still significantly higher than the industry average. Figure 23 Total profit and gross profit margin of sample enterprises in recent years (10000 yuan,%)
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan
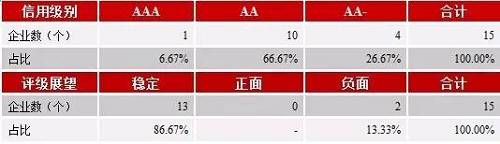
4、 Analysis on the Distribution and Change of Industry Credit Rating in 2016 (1) Distribution and migration of industry credit ratings In 2016, the main credit ratings of the 15 major bond issuing enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry were concentrated between AA -~AAA, of which one was rated AAA, accounting for 6.67% of the total sample; 10 companies rated AA, accounting for 66.67% of the total number of samples; The 4 companies rated AA - accounted for 26.67% of the total number of samples. Among the 15 major bond issuing enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry, 0 have a positive credit rating outlook; 13 stable companies, accounting for 86.67% of the total number of samples; Two negative companies accounted for 13.33% of the total sample. Table 2 Credit Rating and Rating Outlook of Main Bond Issuing Enterprises in the Clothing and Home Textile Industry
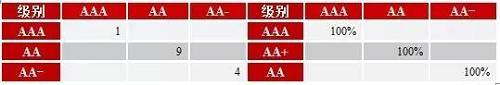
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan In 2016, among the 15 major bond issuing enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry, excluding one enterprise that issued bonds (Jiumu * Co., Ltd.), the main credit rating transfer matrix for the remaining 14 enterprises was prepared. In 2016, the main credit rating of the industry did not change. Table 3 Main Body Level Migration Matrix of the Clothing and Home Textile Industry in 2016
Source: Wind Information, compiled by Peng Yuan
(2) Reason for industry credit level migration From the perspective of credit rating, in 2016, the rating of the clothing and home textile industry did not change. Although the clothing and home textile industry has brought some negative impacts on the credit quality of enterprises in the industry in terms of demand growth, industry competition, and costs, the bond issuing enterprises are basically high-quality enterprises in the industry, with most of them having strong competitive strength and good profitability, and overall operating stability. From the perspective of rating outlook, two companies have downgraded their rating outlook to negative. Among them, Shanghai Metz? Bonway Clothing Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Meibang Clothing") closed some stores in 2015 due to intensified market competition, resulting in a continuous decline in the company's operating income and gross profit. At the same time, the company experienced high expenses during the period, resulting in a loss in its total profit; Shanghai Jialinjie Textile Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Jialinjie") suffered a loss in its total profit in 2015 due to high operating costs and certain pressure on capacity digestion of its proprietary brands.
5、 Industry Credit Outlook
From the perspective of demand, due to the impact of macroeconomic downturn and the adjustment of household consumption structure, the growth rate of domestic clothing and home textile product consumption demand has slowed down; In addition, due to factors such as the slow economic recovery in the United States, Europe, and Japan after the financial crisis, the shift of clothing processing and manufacturing to low-cost countries, and trade friction, China's clothing and home textile industry has faced significant pressure on exports in recent years, and the growth rate of exports has slowed year by year. Overall, the growth rate of demand for clothing and home textile products in China has weakened. From the perspective of market competition, due to the low entry threshold of the clothing and home textile industry, the large number of enterprises in the industry, and the low concentration of the industry, industry competition is increasingly intensifying. In terms of cost, the overall price of clothing fabrics and accessories in China is on the rise, while the rent, channel costs, and labor costs are increasing. Affected by factors such as weak demand and increased costs, the gross profit margin level of China's clothing and home textile industry has declined, and profitability has weakened, but high-quality enterprises in the industry still maintain strong profitability; At the same time, the industry's inventory turnover rate and accounts receivable turnover rate have decreased. The growth rate of the overall debt scale of the clothing and home textile industry continues to decline, and the degree of debt management also shows a downward trend; However, due to the strong financing capacity and low financing costs of high-quality enterprises in the industry, as well as the large demand for business expansion, the degree of debt management of enterprises has increased in recent years, and the pressure on debt repayment has increased. The development of e-commerce will promote enterprises in the clothing and home textile industry to explore new sales channels, and the liberalization of the second child policy will bring certain development opportunities for clothing and home textile enterprises in related fields. |